Understanding the SASB® Standards
The SASB® Standards, now maintained under the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB), play an important role in helping companies apply the ISSB’s general requirements standard, IFRS S1. Specifically, the SASB® Standards help companies identify sustainability-related risks and opportunities, beyond climate-related aspects (which are addressed in IFRS S2), and provide disclosures aligned with investor needs.
This guide to understanding the SASB® Standards is intended to be a useful reference for companies applying the SASB® Standards to develop ISSB Standards disclosures or applying the SASB® Standards on their own. Companies using the SASB® Standards as part of their implementation of ISSB Standards should consider the relevant ISSB guidance. For additional information about how the SASB® Standards support ISSB Standards application, browse our FAQs.
The SASB® Standards are designed to surface the sustainability factors most likely to affect the financial condition or operating performance of companies in a given industry.
As such, the Standards are well-suited to serve as a valuable input to a company’s identification of sustainability-related risks and opportunities. To begin this process, a company may wish to:
- Gain an understanding of the SASB® Standards terminology and structure
- Identify the company’s industry (or industries), using the Sustainable Industry Classification System® (SICS®)
- Review the SASB® Standards for the industry (or industries) most relevant to its activities
- Determine which industry standards and disclosure topics apply
The SASB® Standards group sustainability topics into five “sustainability dimensions”: the environment, human capital, social capital, business model and innovation, and leadership and governance. Of course, the specific activities that drive long-term value creation will necessarily vary from one industry to the next, as well as from company to company. As a result, identifying what a given corporation should disclose requires thoughtful consideration of key issues within the context of the organisation’s unique circumstances. The SASB® Standards are intended to be a useful guide to this process.
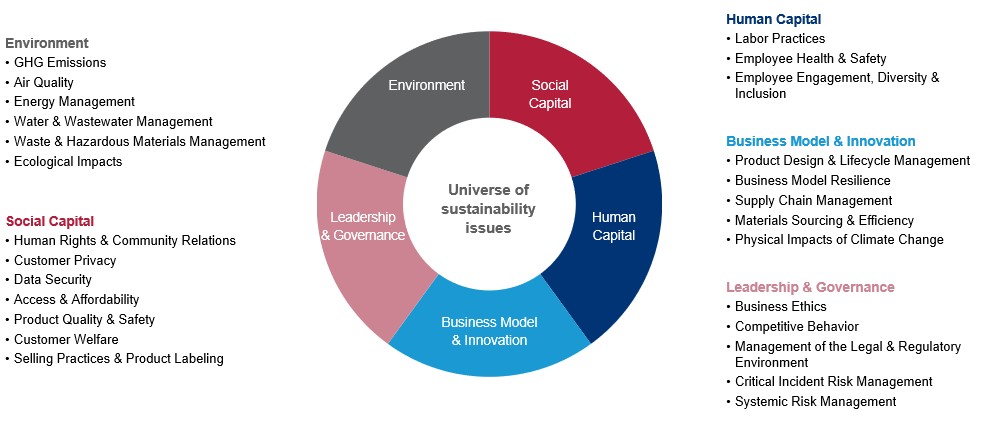


SASB® Standards terminology and structure
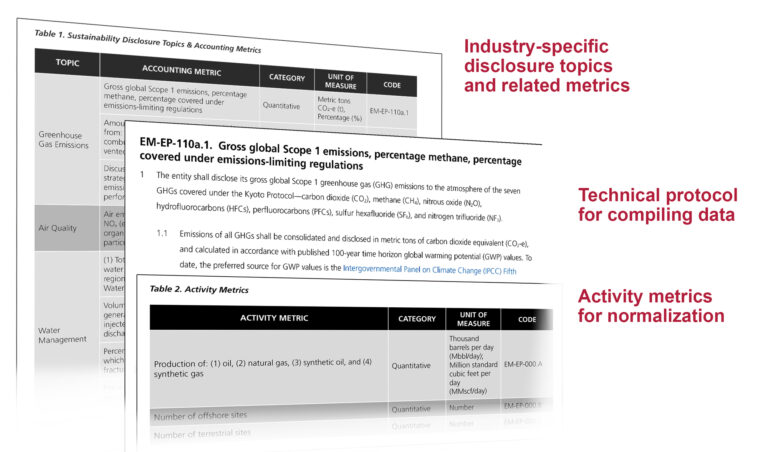
When using the SASB® Standards to identify sustainability-related risks and opportunities, a company can first download the SASB® Standards and then familiarise itself with the following components:
- Disclosure topics: Each SASB® Standard includes a set of disclosure topics, which vary from industry to industry. Disclosure topics describe specific sustainability-related risks or opportunities associated with the activities conducted by entities within a particular industry. On average, the SASB® Standards include six disclosure topics per industry.
- Metrics: Each SASB® Standard provides companies with standardised quantitative and qualitative metrics, which are designed to, either individually or as part of a set, provide useful information regarding a company’s performance in relation to a specific disclosure topic. On average, the SASB® Standards include 13 metrics per industry.
- Technical protocols: Each metric is accompanied by underlying technical protocols that provide guidance on definitions, scope, implementation and presentation of associated metrics. The technical protocols help ensure that metrics are compiled consistently and enable comparisons across companies.
- Activity metrics: Each SASB® Standard includes activity metrics, which quantify the scale of specific activities or operations by a company. Activity metrics are intended for use in conjunction with the metrics to normalise data and facilitate comparison, which are important for the analysis of related disclosures.
Application Guidance: Companies using the SASB® Standards as part of their implementation of ISSB Standards should consider the relevant ISSB application guidance. Specifically, companies should consider paragraphs IG11-24 and IE1-15 in the Accompanying Guidance to IFRS S1.
Companies using the SASB® Standards independently from ISSB Standards may refer to the SASB® Standards Application Guidance.

Determine which industry standards apply
To determine which SASB® Standard (or standards) apply to a company’s operations, it may be helpful to explore the Sustainable Industry Classification System® (SICS®).
Most major industry classification systems use sources of revenue as their basis for classifying companies into specific sectors and industries. Although this approach is valuable for a variety of applications, it does not always group companies that face similar sustainability-related risks or opportunities. SICS® groups like industries based on their sustainability profiles. SICS® builds on and complements traditional industry classification systems by grouping issuers into sectors and industries in accordance with a fundamental view of their business model, their resource intensity and sustainability impacts and their sustainability innovation potential. SICS® presents a new lens through which to assess companies and establish peer groups, by selectively reclassifying existing industries, surfacing new ones and establishing new thematic sectors.
The Materiality Finder is also a useful tool for identifying relevant industry standards. The Materiality Finder offers companies a fast way to browse industry descriptions and disclosure topics. It also allows companies to review and compare disclosure topics from various industries side by side. This tool could be particularly useful for companies that operate in multiple industries.
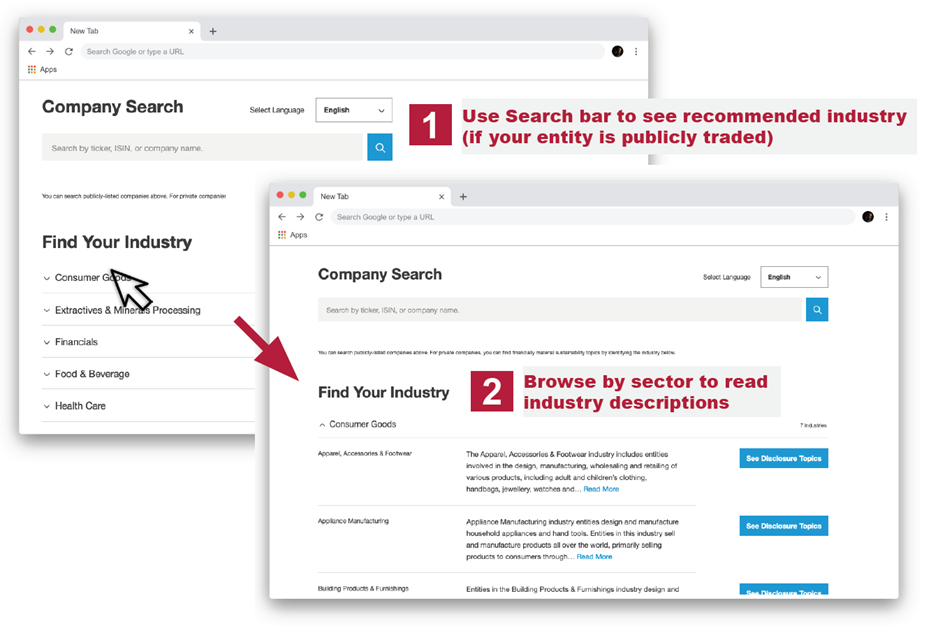

SICS® Lookup Tool
Companies can find out where they are classified within SICS® by using the SICS® Look-Up Tool below, or visit the SICS® Look-Up Tool page for more information. By entering its ticker symbol, publicly listed companies can instantly find their primary SICS® industry and download the appropriate industry standard(s). At this time, companies are classified into a single primary SICS® industry, but that should not prevent companies from using multiple industry standards.
If you are unable to find your company or think the classification needs to be reviewed, please contact us using our classification request form. For any SICS®-related enquiries please visit our enquiry form.
Search for a company using the SICS® Lookup-Tool below:
Questions to consider:
✓ What is your company’s primary industry classification in the SICS® Look-Up Tool?
✓ Which other SICS® industry (or industries) may apply to your company’s operations?
✓ What other companies does your company consider to be its peers or key competitors? In which SICS® industries are they classified?
✓ If your company’s peers have reported using SASB® Standards, which industry standards did they use?
✓ What differences—if any—exist between the company’s primary SICS® industry and its classification in other widely used industry classification systems? What can those differences tell the company about the sustainability risks and opportunities it faces?

Determine which disclosure topics are applicable
After determining your company’s appropriate SICS® industry or industries, the next step is to review the SASB® disclosure topics for each industry and identify which disclosure topics are applicable to your company. Note that because the SASB® Standards are designed to address sustainability factors that are applicable to the typical company within an industry, in some cases they may:
- Include topics that, for certain companies, may not be applicable; and/or
- Not necessarily include every sustainability factor that is applicable to the company.
In other words, the industry standard should not be interpreted as either a “floor” or a “ceiling” for the company’s sustainability disclosure to investors, but instead as a useful guide. For example, the SASB® Standards disclosure topic related to genetically modified organisms in the Chemicals industry may be irrelevant to a company that operates exclusively in the commodity and specialty segments of the industry (i.e., with no exposure to the agricultural segment). Likewise, in the Electric Utilities & Power Generators industry, metrics related to direct (Scope 1) greenhouse gas emissions may be less relevant to a power company that sources—but doesn’t generate—energy.
Similarly, a company may find that additional sustainability disclosure topics not included in its SASB® Standard(s) are relevant to its business strategy based on its specific facts and circumstances. This is especially true for companies with complex or unique business models.
Ultimately, each company is responsible for determining which disclosure topics represent sustainability-related risks and opportunities for its business and which associated metrics to disclose, taking the company’s business model, business strategy and relevant legal requirements into account.

Questions to consider:
✓ Which disclosure topics from which industries appear to be relevant to the company’s prospects over the short, medium and long term?
✓ What sustainability topics have been identified in previous materiality assessments the company may have undertaken? Do the disclosure topics align with previous sustainability-related materiality assessments?
✓ Do the disclosure topics align with the key risks identified in the company’s enterprise risk management (ERM) processes? Are there risks identified in the ERM processes that are not in the SASB® Standards?
✓ Do the disclosure topics align with the key risks identified in the company’s existing risk factor disclosures to investors? Are there risks identified in the risk factors that are not in the SASB® Standards? Which sustainability topics do investors most often ask the company to discuss or disclose?
✓ What sustainability matters that are not included in its SASB® Standard(s) might the company wish to consider disclosing?
What to do if multiple industries apply
Some organisations are “pure play” companies focused on a single line of business that is neatly captured by SICS®. Others’ operations are integrated horizontally across industries or vertically through the value chain straddling multiple industries. For such companies, multiple industry standards may be required to address the full array of sustainability topics reasonably likely to impact a firm’s prospects over the short, medium and long term. For example:
- If a company’s consolidated operations span multiple industries, it may be necessary to review multiple industry standards to identify topics beyond those defined in its primary industry standard that may warrant disclosure to investors.
- If a company has a unique business model that defies traditional industry classifications, it may wish to consider disclosure topics (and associated metrics) from an array of industries that have similar activities, choosing those disclosure topics most likely to communicate material information to investors. Some companies with very unique business models, such as emerging technology-based business models, may need to create a custom “SASB® template” based on disclosure topics from multiple industries.

The SASB® Standards include a unique sustainability standard for each of 77 SICS® industries. Thus, for companies that are vertically or horizontally integrated across more than one industry, reporting with the SASB® Standards may initially appear challenging. Companies that have faced similar challenges can provide helpful guidance on how to best overcome this perceived hurdle. For example, Roger Seabrook, VP Finance Marketing & Sustainability at Unilever, noted, “Our portfolio includes diverse products such as ice cream, tea, deodorant and soap, so we don’t fit neatly” into one industry or another. That being said, he suggests, you can’t become paralysed by the range of standards that may apply to your company’s operations. “You’ve got to start somewhere,” Seabrook said. “Focus on one area that is really important to the business” and go from there.
Kristin Peterson, ESG Director at Kinder Morgan, agreed. Her company operates in a range of extractive and transportation industries, so “when we pulled all the metrics together from five to six standards, it looked overwhelming at first.” She recommends a methodical approach: determining which industries are applicable, consolidating the metrics from those industries, then looking for overlap—including where related metrics are consistent or not. By using the company’s subject matter experts to help assess the metrics, identify those already being collected, and formulate plans for the rest, “we were able to wean down the list to something considerably more manageable” and make progress, she said.
Many companies that have implemented SASB® Standards have used multiple industry standards to provide investors with a complete picture of their performance on sustainability-related risks and opportunities. Feedback from several companies suggests that the following approach may be helpful when assessing which industry standards apply, and subsequently in using those standards to disclose information:
- Map the company’s activities to the applicable SICS® industries
- For applicable SICS® industries, evaluate the topics in each industry standard to determine which are applicable
- Prioritise reporting of these topics based on the informational needs of investors as well as the cost-effectiveness of obtaining and reporting the associated data
- Prioritise reporting of topics based on relative size of business segments and/or relative risk (e.g., relatively small business segments can have outsize contributions to risk)
Your company, your call
SASB® Standards are intended for use in communications to investors regarding sustainability-related risks and opportunities that are likely to affect a company’s prospects over the short, medium and long term. However, reporting with the SASB® Standards is not an “all or nothing” proposition. A company determines for itself which standard or standards are applicable, which disclosure topics are relevant and which associated metrics to report, taking relevant legal requirements into account.

